Modern software teams are under constant pressure to ship faster without compromising stability. Customers expect frequent updates, seamless performance, and zero disruptions. This is where DevOps best practices play a critical role—bridging the gap between development and operations to enable faster deployments while significantly reducing downtime.
When implemented correctly, DevOps is not just a technical improvement but a business advantage.
Why DevOps Matters for Modern Businesses
Traditional deployment processes are often slow, manual, and error-prone. Delays in releases, unexpected outages, and rollback failures can directly impact revenue and customer trust.
DevOps introduces automation, collaboration, and continuous feedback loops that allow teams to deploy confidently and recover quickly when issues arise.
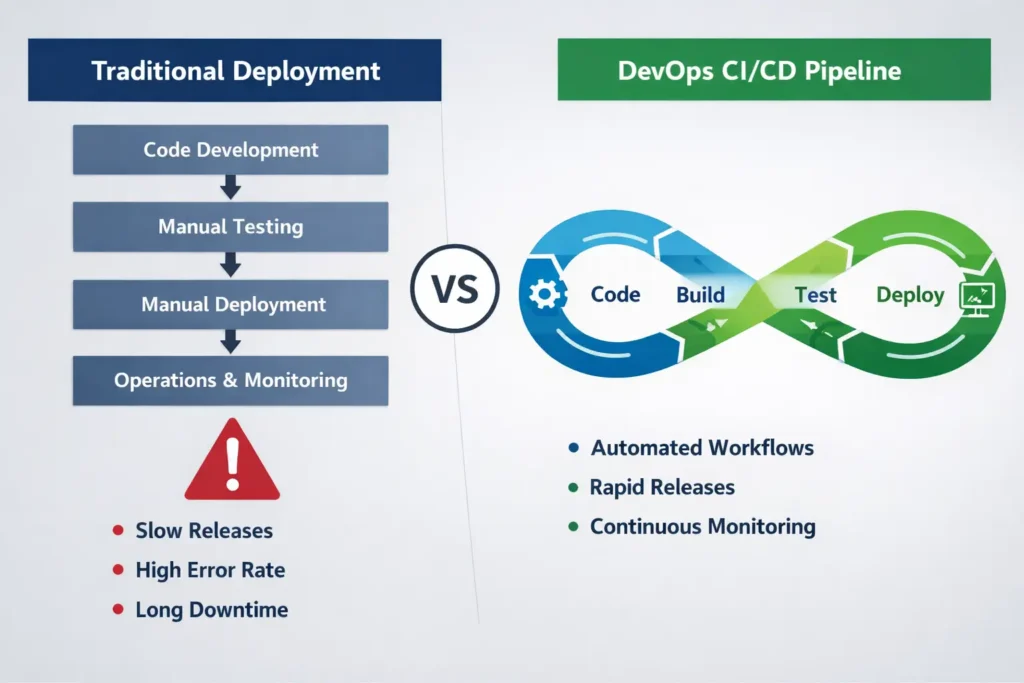
1. Automate CI/CD Pipelines
One of the most effective DevOps practices is building automated Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Automation ensures that:
- Code is tested consistently
- Builds are repeatable
- Deployments happen faster with fewer errors
By removing manual intervention, teams can deploy updates multiple times a day with confidence while maintaining high quality standards.
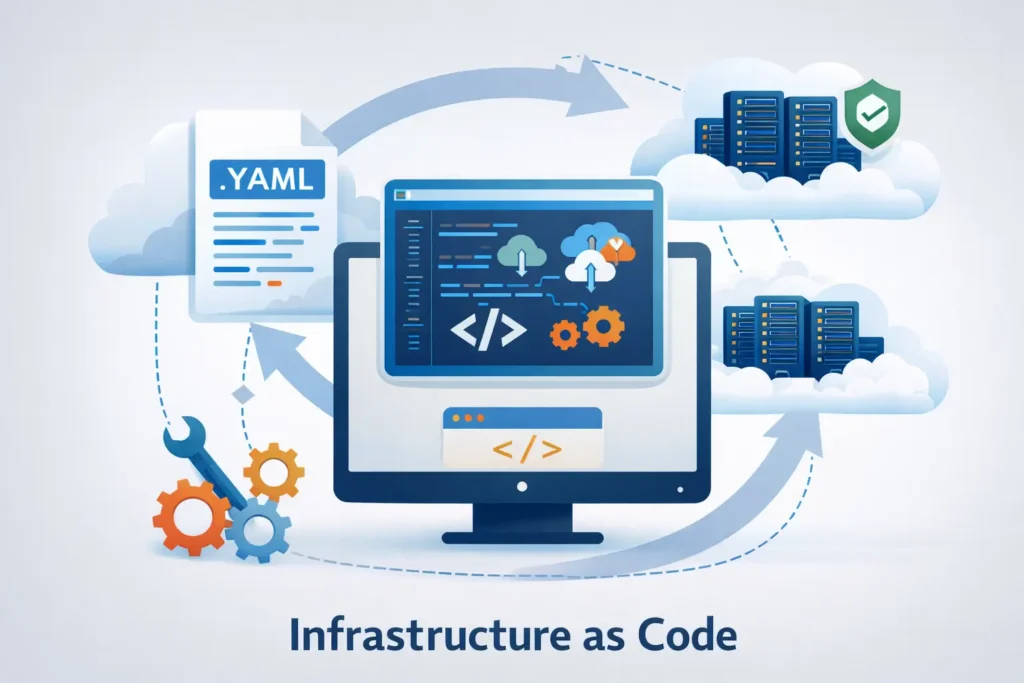
2. Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
Managing infrastructure manually often leads to inconsistencies across environments. Infrastructure as Code solves this by defining servers, networks, and configurations in version-controlled files.
Benefits include:
- Faster environment setup
- Reduced configuration drift
- Easier scaling across cloud platforms
IaC also improves disaster recovery by allowing infrastructure to be recreated quickly when needed.
3. Implement Continuous Monitoring and Logging
You can’t fix what you can’t see. Continuous monitoring helps teams detect performance issues, errors, and unusual behavior before users are affected.
Effective monitoring strategies include:
- Application performance monitoring
- Log aggregation and analysis
- Real-time alerts for critical metrics
This proactive approach minimizes downtime and speeds up incident resolution.
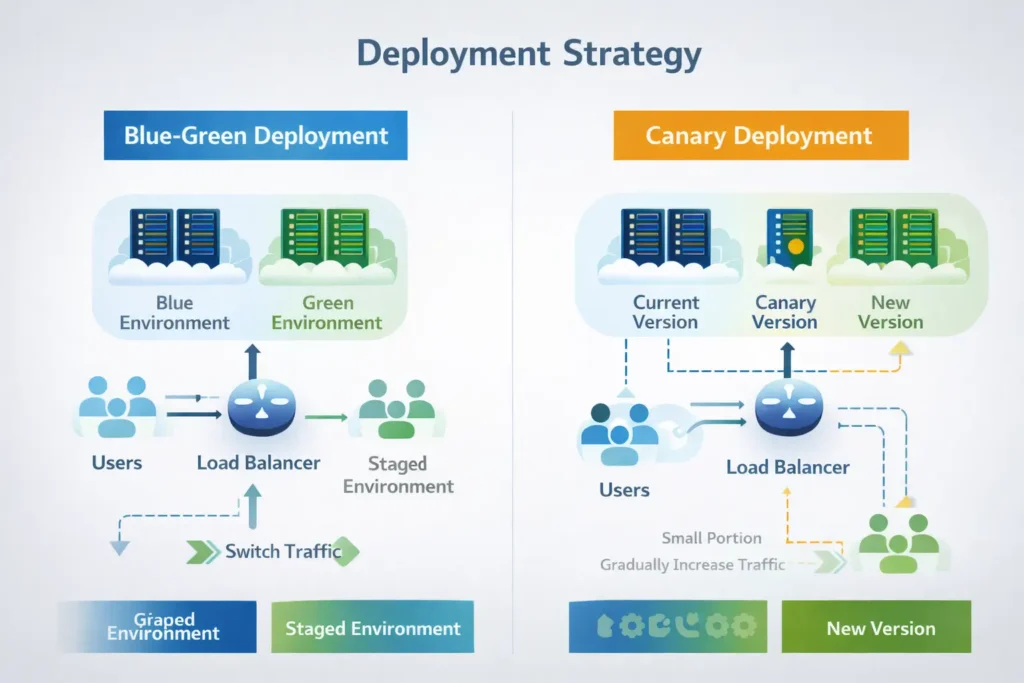
4. Deploy Incrementally with Rollback Strategies
Large, infrequent releases increase risk. DevOps teams focus on smaller, incremental deployments that are easier to test and roll back.
Best practices include:
- Blue-green deployments
- Canary releases
- Automated rollback mechanisms
These techniques allow teams to release features safely while protecting system stability.
5. Foster Collaboration Between Teams
DevOps is as much about culture as it is about tools. Strong collaboration between developers, operations, and QA teams reduces bottlenecks and improves accountability.
Shared ownership of performance and reliability leads to:
- Faster problem resolution
- Better communication
- Higher-quality releases
Conclusion
DevOps best practices enable businesses to deploy faster, reduce downtime, and build resilient systems that scale with growth. By investing in automation, monitoring, and collaboration, organizations can transform their delivery pipelines into a competitive advantage.


